The stock market crash caused the great depression. true false
Great Depression , worldwide economic downturn that began in and lasted until about It was the longest and most severe depression ever experienced by the industrialized Western world, sparking fundamental changes in economic institutions, macroeconomic policy, and economic theory. Although it originated in the United States , the Great Depression caused drastic declines in output, severe unemployment , and acute deflation in almost every country of the world.
Its social and cultural effects were no less staggering, especially in the United States, where the Great Depression represented the harshest adversity faced by Americans since the Civil War.
The timing and severity of the Great Depression varied substantially across countries. The Depression was particularly long and severe in the United States and Europe ; it was milder in Japan and much of Latin America.
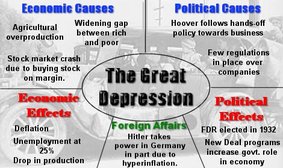
Perhaps not surprisingly, the worst depression ever experienced by the world economy stemmed from a multitude of causes. Declines in consumer demand , financial panics , and misguided government policies caused economic output to fall in the United States, while the gold standard , which linked nearly all the countries of the world in a network of fixed currency exchange rates , played a key role in transmitting the American downturn to other countries.
The recovery from the Great Depression was spurred largely by the abandonment of the gold standard and the ensuing monetary expansion. The economic impact of the Great Depression was enormous, including both extreme human suffering and profound changes in economic policy.
The Great Depression began in the United States as an ordinary recession in the summer of The downturn became markedly worse, however, in late and continued until early Real output and prices fell precipitously.
stock market crash of | American history | omenejomy.web.fc2.com
Between the peak and the trough of the downturn, industrial production in the United States declined 47 percent and real gross domestic product GDP fell 30 percent. The wholesale price index declined 33 percent such declines in the price level are referred to as deflation. Although there is some debate about the reliability of the statistics, it is widely agreed that the unemployment rate exceeded 20 percent at its highest point.
Moreover, during the —82 recession prices continued to rise, although the rate of price increase slowed substantially a phenomenon known as disinflation. The Depression affected virtually every country of the world. However, the dates and magnitude of the downturn varied substantially across countries.
Great Britain struggled with low growth and recession during most of the second half of the s. Britain did not slip into severe depression, however, until early , and its peak-to-trough decline in industrial production was roughly one-third that of the United States. France also experienced a relatively short downturn in the early s. The French recovery in and , however, was short-lived. French industrial production and prices both fell substantially between and The decline in German industrial production was roughly equal to that in the United States.
A number of countries in Latin America fell into depression in late and early , slightly before the U. While some less-developed countries experienced severe depressions, others, such as Argentina and Brazil , experienced comparatively mild downturns. Japan also experienced a mild depression, which began relatively late and ended relatively early. Dates of the Great Depression in various countries in quarters country depression began recovery began United States The general price deflation evident in the United States was also present in other countries.
Virtually every industrialized country endured declines in wholesale prices of 30 percent or more between and Because of the greater flexibility of the Japanese price structure, deflation in Japan was unusually rapid in and This rapid deflation may have helped to keep the decline in Japanese production relatively mild. The prices of primary commodities traded in world markets declined even more dramatically during this period.
For example, the prices of coffee, cotton, silk, and rubber were reduced by roughly half just between September and December As a result, the terms of trade declined precipitously for producers of primary commodities. Output grew rapidly in the mids: Output had fallen so deeply in the early years of the s, however, that it remained substantially below its long-run trend path throughout this period. In —38 the United States suffered another severe downturn, but after mid the American economy grew even more rapidly than in the mids.
Recovery in the rest of the world varied greatly. The British economy stopped declining soon after Great Britain abandoned the gold standard in September , although genuine recovery did not begin until the end of The economies of a number of Latin American countries began to strengthen in late and early Germany and Japan both began to recover in the fall of Canada and many smaller European countries started to revive at about the same time as the United States, early in On the other hand, France, which experienced severe depression later than most countries, did not firmly enter the recovery phase until Articles from Britannica encyclopedias for elementary and high school students.
During the s much of the world faced harsh economic conditions. Many people were out of work, hungry, or homeless. This period is called the Great Depression.
Famous and Powerful of
It started in the United States, but it quickly spread throughout the world. United States President Franklin D.
Roosevelt, in his first inaugural address, made some attempt to assess the enormous damage: More important, a host of unemployed citizens face the grim problem of existence, and an equally great number toil with little return. We welcome suggested improvements to any of our articles. You can make it easier for us to review and, hopefully, publish your contribution by keeping a few points in mind. You may find it helpful to search within the site to see how similar or related subjects are covered.
Any text you add should be original, not copied from other sources.
At the bottom of the article, feel free to list any sources that support your changes, so that we can fully understand their context. Internet URLs are the best. Your contribution may be further edited by our staff, and its publication is subject to our final approval. Unfortunately, our editorial approach may not be able to accommodate all contributions. Our editors will review what you've submitted, and if it meets our criteria, we'll add it to the article.
Please note that our editors may make some formatting changes or correct spelling or grammatical errors, and may also contact you if any clarifications are needed. Spotlight Demystified Quizzes Galleries Lists On This Day Biographies. What are you looking for? You have reached Britannica's public website. For ad-free access to your Britannica School or Library account Click here.
Depression of , Slump of View All Media Date - c. Dates of the Great Depression in various countries in quarters. Peak-to-trough decline in industrial production in various countries annual data. Journey Around the World. Next page Causes of the decline.
Additional Media View all media. More about Great Depression 83 References found in Britannica Articles. The Hollywood studio system in history of the motion picture: Introduction of colour in history of the motion picture: The Hollywood studio system. Digital History - The Human Meaning of the Great Depression Library of Economics and Liberty -The Concise Encyclopedia of Economics - The Great Depression New Georgia Encyclopedia - History and Archaeology - Great Depression Public Broadcasting Service - American Experience - The Crash of Public Broadcasting Service - The Great Depression Texas State Historical Association - The Handbook of Texas Online - Great Depression The Canadian Encyclopedia - Great Depression U.
Department of State - Office of the Historian - The Great Depression and U. Foreign Policy United States History - The Great Depression University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign - Department of English - Modern American Poetry - About the Great Depression World History International Project - The Great Depression.
Help us improve this article! Contact our editors with your feedback. Introduction Economic history Timing and severity Causes of the decline Sources of recovery Economic impact Culture and society in the Great Depression Global concerns Political movements and social change New forms of cultural expression Portrayals of hope.
Keep Exploring Britannica The Bluest Eye. Take this History True or False Quiz at Encyclopedia Britannica to test your knowledge of Pakistan, the Scopes monkey trial, and more historic facts.
A Study of History: Who, What, Where, and When? Take this History quiz at encyclopedia britannica to test your knowledge of various facts concerning world history and culture. Take this History True or False Quiz at Encyclopedia Britannica to test your knowledge of bridges, air travel, and more historic facts. Its most notable feature is a French Renaissance mansion that is considered the largest You have successfully emailed this.
Tips for Editing Leave Edit Mode Submit.

Thank You for Your Contribution! There was a problem with your submission.
1) Examine the relationship between the Great Depression and the World War II. - INSIGHTS
Please try again later. Home Spotlight Demystified Quizzes Galleries Lists On This Day Biographies Login Join.

View All Media 21 Images, 4 Videos. If you prefer to suggest your own revision of the article, you can go to edit mode requires login. Thank you for your feedback.